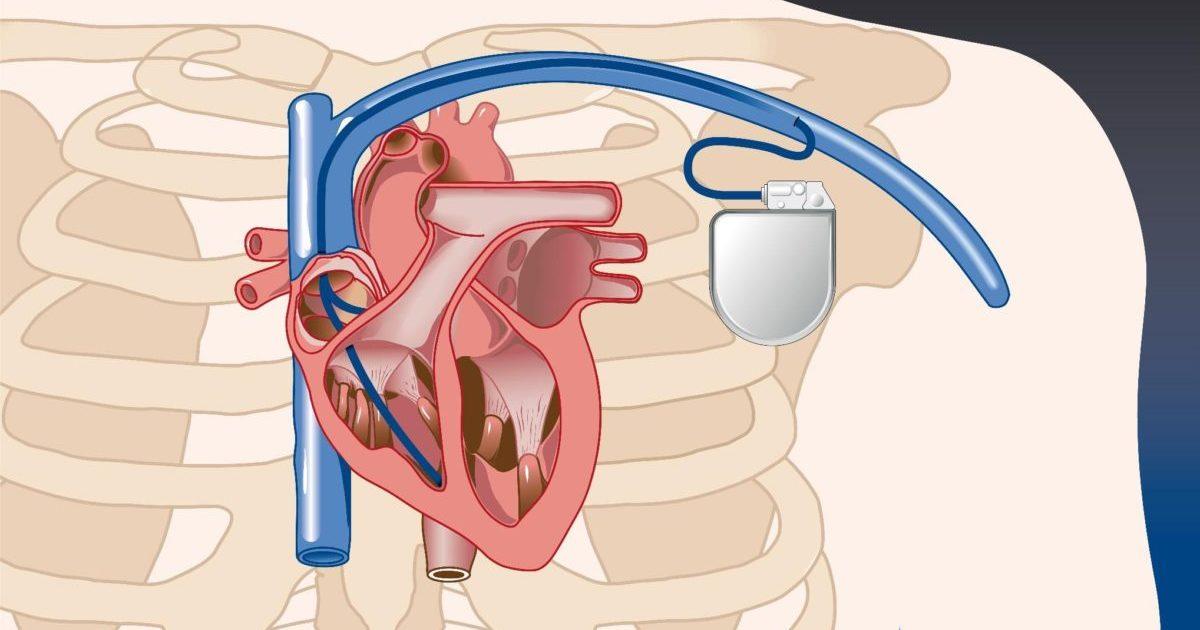
There are different types of pacing leads that are used depending on where they need to be placed in the heart and the type of pacing required.
Transvenous Leads
Transvenous leads are the most common type used today. They are inserted through a vein into the heart where the tip anchors in the heart muscle. There are three main types:
- Atrial leads - Used for atrial pacing and placed in the right atrium.
- Ventricular leads - Used for ventricular pacing and placed in the right ventricle.
- Biventricular leads - Have electrodes that pace both ventricles and are used for cardiac resynchronization therapy to treat heart failure.
Epicardial Leads
Epicardial leads are temporary Cardiac Pacing Leads directly on the surface of the heart during surgery before being connected to an external pacemaker. They are mainly used for post-operative pacing in patients who are at risk of developing heart block.
Insertable Cardiac Monitor Leads
Insertable cardiac monitor leads are used to detect and monitor heart rhythm abnormalities for an extended period without requiring the patient to wear an external monitor belt. The small monitor and lead system is inserted just under the skin in a minor procedure.
Lead Placement and Extraction
Proper placement of pacing leads is crucial for optimal pacing and sensing. Imaging like fluoroscopy is used during insertion to guide the leads into position. Over time, leads can become displaced, fractured or infected requiring extraction. Lead extraction is a specialized procedure using specialized sheaths and tools to remove leads that are no longer serving their purpose.
Lead Performance and Lifespan
The performance of a pacing lead depends on various design factors like insulation material, conductor wire, and anchoring mechanism. Modern pacing leads are expected to function reliably for 5-10 years on average before needing replacement, usually due to insulation breakdown or conductor fractures. Regular follow-ups help monitor lead parameters and flag issues requiring intervention.
Lead Parameters and Threshold Testing
During device implantation and follow-ups, lead parameters are measured to ensure proper performance. Tests like threshold testing, impedance monitoring and sensing checks are done. Threshold testing determines the minimum current required to pace the heart (capture threshold) which is an indicator of lead health - a rising threshold suggests deterioration. Impedance checks for any increase due to insulation defects. Sensing looks for adequate amplitude of intrinsic signals being detected. Together these parameters provide information on lead integrity over time for the implanter to factor in replacement decisions.
Get more insights on Cardiac Pacing Leads
Cardiac Pacing Leads: New Study Highlights Importance of Advanced Cardiac Pacing