In recent years, the global energy landscape has been shifting towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives. Among these alternatives, hydrogen has emerged as a promising contender in the quest for a cleaner future. With its versatile applications and zero-emission properties, hydrogen is revolutionizing industries and paving the way for a greener tomorrow. In this article, we will explore the hydrogen market, its significance, current state, production methods, applications, challenges, government initiatives, key players, market trends, and future outlook.
Introduction to the Hydrogen Market
The hydrogen market refers to the production, storage, and distribution of hydrogen as an energy source. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and can be obtained from various sources, including fossil fuels, water, and biomass. Its versatile nature, clean combustion properties, and ability to be used as an energy carrier make it an attractive option for a wide range of applications.
The Significance of Hydrogen as an Energy Source
Hydrogen offers several advantages as an energy source. Firstly, it produces no greenhouse gas emissions when used in fuel cells or burned in engines, making it an excellent solution for combating climate change. Secondly, hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources, such as wind and solar power, making it a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Lastly, hydrogen can be stored and transported easily, allowing for greater flexibility in energy distribution.
Current State of the Hydrogen Market
The hydrogen market is still in its early stages but is experiencing rapid growth and development. Several countries, including the United States, Japan, and Germany, have recognized the potential of hydrogen and are investing heavily in its research, development, and deployment. The market is witnessing increased collaborations between governments, industry players, and research institutions to accelerate the adoption of hydrogen technologies.
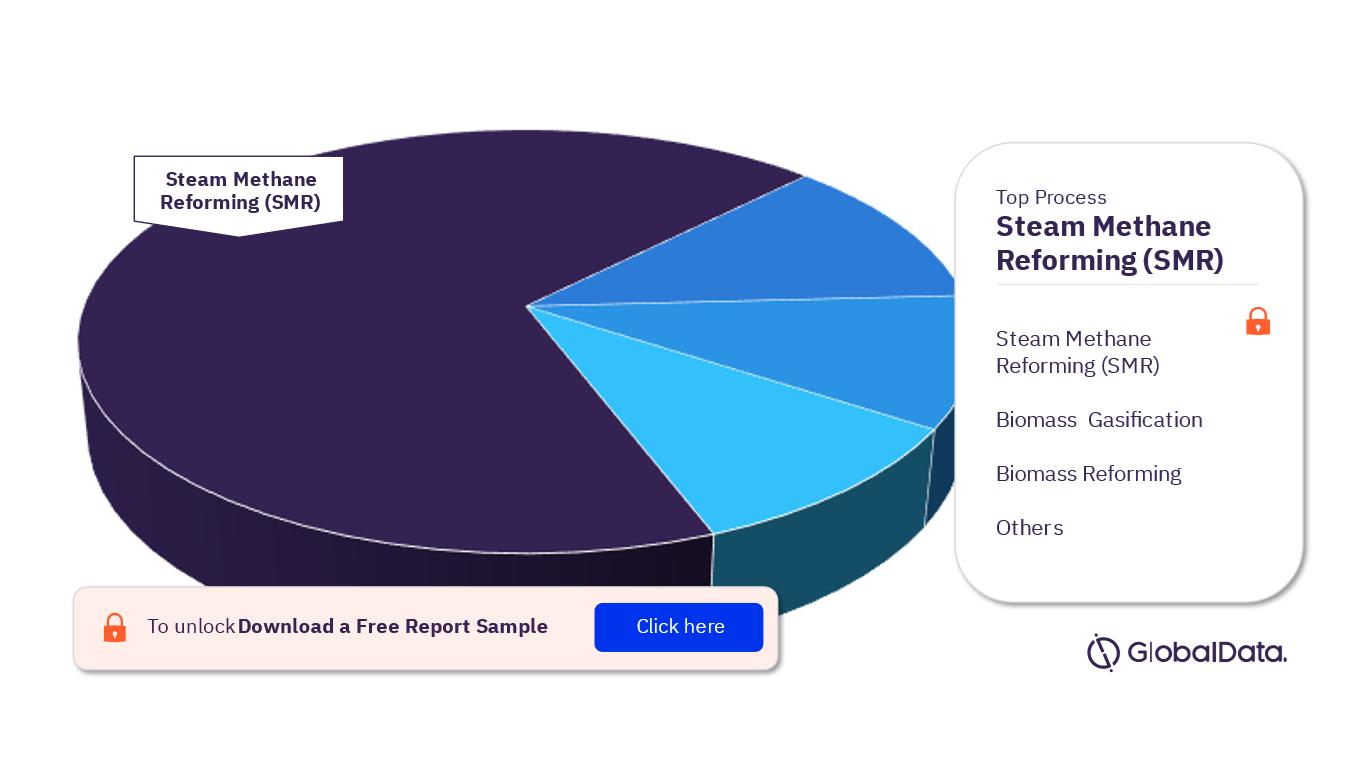
Hydrogen Production Methods
There are several methods for producing hydrogen, each with its own advantages and limitations. The most common methods include:
Steam Methane Reforming (SMR)
SMR is the most widely used method for hydrogen production, accounting for the majority of the global hydrogen supply. It involves the reaction of natural gas with high-temperature steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. While SMR is cost-effective, it is currently reliant on fossil fuels, resulting in carbon emissions.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a process that uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. It can utilize renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, making it a sustainable option. However, electrolysis is currently more expensive than SMR and requires further advancements in technology to become more cost-effective.
Biomass Gasification
Biomass gasification involves the conversion of organic materials, such as agricultural residues and forestry waste, into hydrogen-rich gas through a thermochemical process. This method provides a sustainable option for hydrogen production, utilizing biomass that would otherwise go to waste.
For more insights into the low-carbon hydrogen market segments by process, download a free report sample